Biological basis
... for professional growing systems
Microbiology as the foundation of economic aquaponics and hydroponics
In modern aquaponics and hydroponics facilities, biology determines the success or failure of the operation. While the technology is visible, the actual top performers work invisibly: millions of microorganisms that create the basis for profitable and sustainable production through their metabolic processes.
The nitrogen cycle as the heart of the system
For agricultural businesses that rely on aquaponics, the understanding of the Nitrification essential. Specialized bacterial strains (Nitrosomonas And Nitrobacter) convert fish excreta into plant-available nutrients. This biological conversion is the core of economic efficiency: without functioning nitrification there are no healthy plants, without healthy plants there are no yields.
Optimizing these processes can increase nutrient efficiency by 200-400% while dramatically reducing dependence on external fertilizers.
Professional microbiome management
In these specialist articles you will find out:
Systems biology for production optimization
- Establishment and monitoring of stable bacterial populations in large-scale facilities
- Indicators of biological system health and their measurement
- Strategies for accelerating system entry (start-up phase)
Biological quality control
- Microbiological parameters for constant product quality
- Preventive biological pest and disease control
- Integration of beneficial insects into the overall system
Business aspects of biology
- Cost savings through biological process optimization
- Reduction of downtime through stable microbiome
- Longer plant life due to biological balance
Scalable solutions: From small businesses to large systems
For specialized garden centers and small agricultural businesses
Understand how biological principles provide economic benefits even in smaller, professional facilities (50-500 m²). Learn tried and tested methods for building robust biological systems without high investment costs.
For large companies and industrial systems
Learn how complex biological processes are monitored, controlled and optimized in production facilities with several thousand square meters. From automated measurement systems to microbiological intervention strategies.
Scientifically based, practice-oriented
Measurement and monitoring techniques
- Relevant parameters for process monitoring
- Cost-efficient analysis methods for everyday operations
- Early warning systems for biological disorders
Troubleshooting biological systems
- Diagnosis and correction of disturbances in the nitrogen cycle
- Restoration of biological balance after failures
- Preventive measures against systemic problems
Integration into existing operational processes
- Adaptation of biological cycles to production schedules
- Seasonal optimization of microbiology
- Staff training for biological systems support
Economic efficiency through biology
The biological basis is not only scientifically interesting, but directly business-relevant:
- Yield increases from 15-30% through optimized nutrient management
- Cost savings for fertilizers of up to 80%
- Reducing of plant protection products by an average of 90%
- Amelioration of product quality and durability
Understanding future-proof technology
Modern agricultural businesses that invest in sustainable production systems require a sound understanding of biological processes. This is the only way to successfully operate systems in the long term and continuously optimize them.
This article provides the necessary expertise for operational decisions and strategic further development of biology-based cultivation systems.
Professional aquaponics and hydroponics begins with understanding microbiology – the foundation for sustainable operational success.
KAT ID: 11Subcategories
Ecoponic

Core elements of ecoponics
Use of organic nutrient solutions
In contrast to conventional hydroponic systems, which often rely on synthetic fertilizers, ecoponics uses organic nutrient solutions. These are derived from natural sources such as compost tea, worm compost extract or other organic waste.
Sustainable resource management
Ecoponic systems are designed to use water and nutrients efficiently. By reusing and recycling water and nutrients, the ecological footprint is minimized.
Promoting biodiversity
Ecoponics promotes biodiversity by integrating different plant species and creatures (snails, cockroaches, earthworms, guppies, etc) into a system. This can help to control pests and diseases and maintain the ecological balance.
Energy efficiency
By using renewable energy and energy-efficient technologies, ecoponics aims to reduce energy consumption and minimize environmental impact.
Instead of chemical pesticides, ecoponic systems use biological pest control methods such as beneficial insects or biological preparations.
Advantages of ecoponics
- Environmentally friendly: By not using synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, the environment is less polluted.
- Resource-efficient: The efficient use of water and nutrients helps to conserve natural resources.
- Healthy food production: The use of organic nutrients leads to healthier plants and therefore healthier food.
- Promoting sustainability: Ecoponic systems support sustainable agricultural practices and contribute to the preservation of natural ecosystems.
While ecoponics as a concept is gaining momentum, there is less comprehensive scientific literature on it compared to aquaponics and hydroponics. For further information, specialized publications and case studies of organic farms may be helpful. A useful book could be "The Organic No-Till Farming Revolution" by Andrew Mefferd, which describes sustainable farming practices in detail, although it does not focus exclusively on ecoponics.
Fish

It's all about the right fish!
The availability of stocked fish is a crucial criterion for the operation, which can significantly limit the choice of fish species. Orientate yourself on this first!
In addition, it must be expected at the beginning that the system will need a certain amount of time to stabilize. However , according to fisheries experts from LANUV and the ministry, practical experience shows that new systems only produce around 10% - 30% of the maximum possible biomass in the first few years. In stable operation, recirculation systems are operated at approx. 70% - 80% of their capacity.
In order to find the right fish for your own aquaponics system, you can already rely on a large selection of suitable food fish. There are small fish for small systems, big ones for larger systems. However, they all have to meet some basic requirements. As a rule, fish are used that can withstand the high, almost tropical temperatures in a facility. So they have to be heat resistant. Furthermore, they have to get along with many other animals in a small space. This requires the fish to have a certain resistance to stress, which enables breeders to keep, manipulate and care for the fish conscientiously and without hesitation.
One of the greatest dangers resulting from open aquaculture farming is the transmission of diseases and the transfer of genetic material from farmed fish to wild fish. This happens when fish escape from aquaculture and come into contact with wildlife. Since the systems in aquaponics form a closed circuit and are located far away from wild fish areas, there is no genetic crossing of farmed fish with wild fish. Another factor that has a strong positive effect on the use of aquaponics. So which species are suitable for aquaponics?
Below we have listed all the relevant key data for various fish species, which can narrow down your selection for your purposes based on growth, breeding time, temperature range and many other factors.
| Please understand that we only share this information with our customers. Therefore only the first entry in our database is displayed. A list of data for fish in Aquaponik can be found here in german. |
Medicinal Plant
 Medicinal plants in hydroponics – opportunities for research and small-scale cultivation – potential and limitations
Medicinal plants in hydroponics – opportunities for research and small-scale cultivation – potential and limitationsThe hydroponic cultivation of medicinal plants enables precise control of environmental parameters and can contribute to the standardization of active ingredient content. In addition to potential advantages for industrial production, such as greater independence from climatic and geographical restrictions, applications in small-scale cultivation are also being discussed. Such systems could enable the local supply of medicinal plants and serve niche markets. Nevertheless, there are considerable scientific and technical challenges. These include, in particular, the insufficiently researched influences of hydroponic cultivation conditions on the synthesis of secondary metabolites, as well as high requirements for hygiene and contamination control in closed systems. In addition, the economic viability of small-scale hydroponic systems must be critically evaluated in comparison to established production methods.
Microgreens (en)
Microgreens - small plants with a big impact
Microgreens are edible young vegetables that are harvested shortly after the “cotyledon” phase. Cotyledon is a phase in the early embryological development of a plant in which the first leaves develop in the seed germ. A short time later, the germ opens and the first leaves emerge from the soil. The precursor to microgreens are sprouts.
 This is the time when you can harvest the young green leaves. It is full of high-quality nutrients and contains more proteins than older plants. In short - microgreens are a true superfood. However, a distinction should be made between microgreens and sprouts. Sprouts grow without daylight and without soil, but microgreens require soil as a growing medium and always sunlight. Furthermore, microgreens contain far more chlorophyll than sprouts because they have already formed leaves.
This is the time when you can harvest the young green leaves. It is full of high-quality nutrients and contains more proteins than older plants. In short - microgreens are a true superfood. However, a distinction should be made between microgreens and sprouts. Sprouts grow without daylight and without soil, but microgreens require soil as a growing medium and always sunlight. Furthermore, microgreens contain far more chlorophyll than sprouts because they have already formed leaves.
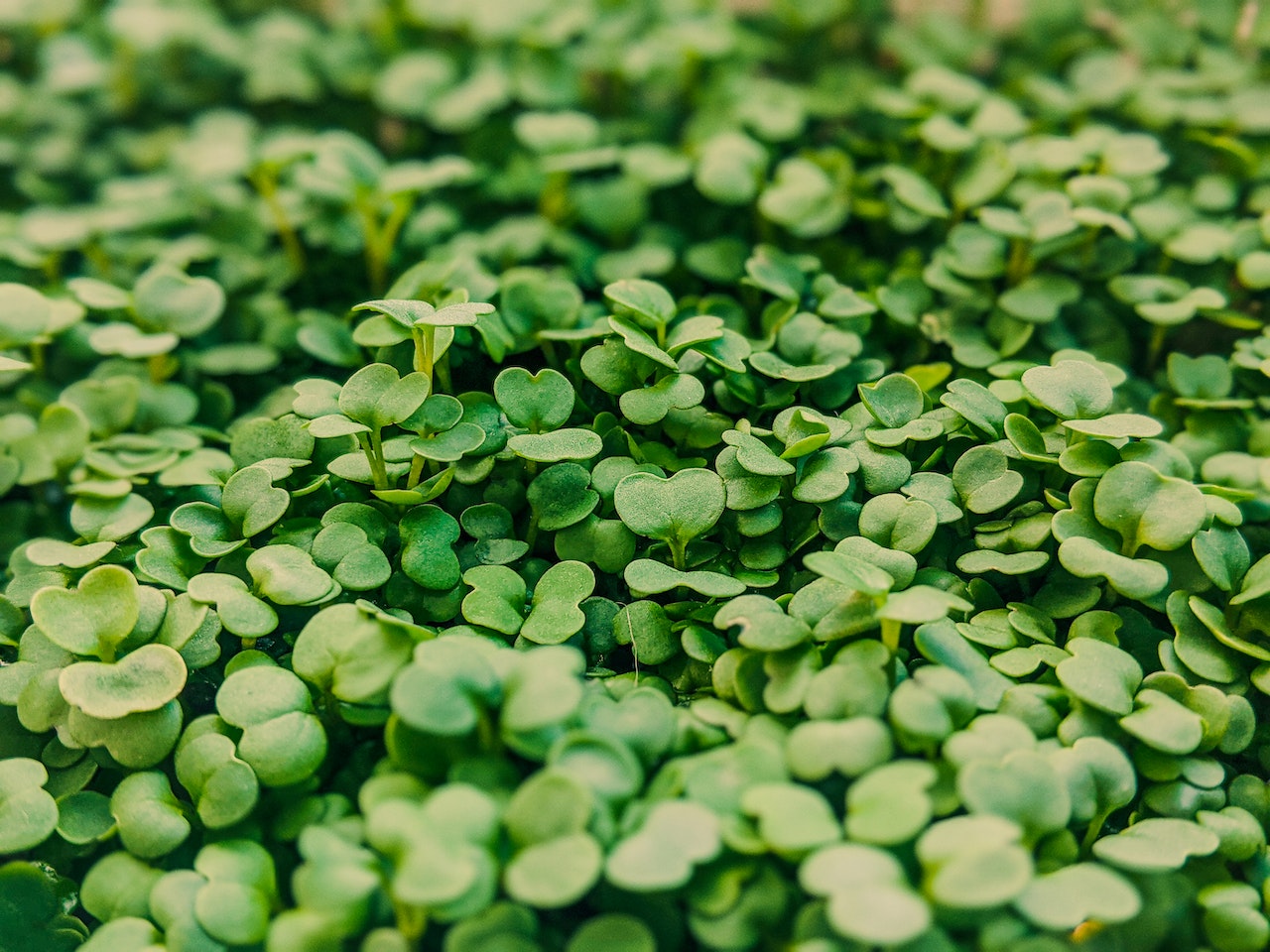 Microgreens have originally been cultivated and grown in Southern California since the 1990s. The career continued to East America via San Francisco, so the little plants have come a long way and are now an integral part of modern cuisine and conscious nutrition. In the beginning, arugula, beetroot, cress, basil and cilantro were grown in America. Today there are hardly any limits to microgreens, but seeds from the nightshade family, such as tomatoes or potatoes, should not be used because their young leafy greens contain toxins.
Microgreens have originally been cultivated and grown in Southern California since the 1990s. The career continued to East America via San Francisco, so the little plants have come a long way and are now an integral part of modern cuisine and conscious nutrition. In the beginning, arugula, beetroot, cress, basil and cilantro were grown in America. Today there are hardly any limits to microgreens, but seeds from the nightshade family, such as tomatoes or potatoes, should not be used because their young leafy greens contain toxins.
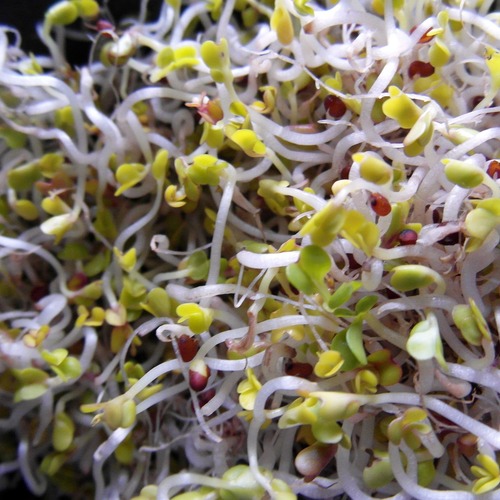 The favorites among the microgreens can vary depending on taste, one leaf green is a little spicier, the other tastes mildly sour, but they all have one thing in common - they are packed with vitamins, trace elements and proteins right down to the tips of the leaves. Commonly grown microgreens include red cabbage, coriander, amaranth, radish, beetroot or cress. So how can aquaponics / hydroponics be combined with microgreens?
The favorites among the microgreens can vary depending on taste, one leaf green is a little spicier, the other tastes mildly sour, but they all have one thing in common - they are packed with vitamins, trace elements and proteins right down to the tips of the leaves. Commonly grown microgreens include red cabbage, coriander, amaranth, radish, beetroot or cress. So how can aquaponics / hydroponics be combined with microgreens?
Aquaponics is excellent for growing microgreens. Optimal conditions can be created in greenhouses that enable weekly harvesting. Microgreens can cope with regular daylight, so it is possible to use fish that can withstand medium and high temperatures if the fish are kept in the greenhouse with the plants.  If the fish farm is housed in a separate and cool building, the types of fish can be adapted to the conditions. You can find a selection of fish species for aquaponics here . In addition to choosing the right fish, it also depends on what characteristics the greenhouse should have.
If the fish farm is housed in a separate and cool building, the types of fish can be adapted to the conditions. You can find a selection of fish species for aquaponics here . In addition to choosing the right fish, it also depends on what characteristics the greenhouse should have.
There are a multitude of possibilities, the limits of which are only set by the imagination. Since the water used comes from the closed cycle of aquaponics/hydroponics, it is free of pesticides and fertilizers and the system can be operated all year round, resulting in a regulated yield of microgreens and fish.
KAT ID: 29
Plants
Which plants grow in aquaponics or hydroponics?

Push & Pull (en)
Push & Pull Strategies
An innovative approach for sustainable plant protection in hydroponic systems

Preface: Nature as a Model
In natural ecosystems, a fascinating balance exists between plants and pests. Push & Pull utilizes these very natural mechanisms to protect crops in an elegant way. Instead of working against nature, we harness its principles.
This approach revolutionizes plant protection in hydroponic systems, where conventional methods often reach their limits. Through the combined effect of repellent and attractive strategies, we create an intelligent system that strategically directs pests rather than simply fighting them.
The Basic Principle of the Push & Pull Approach
Push & Pull is an innovative concept in integrated pest management that keeps pests away from the main crop through a combined repellent and attractive effect.
PUSH Principle
Repellent Effect: Special plants or substances repel pests from the main crop.
- Essential oils as natural repellents
- Botanical insecticides
- Scent compounds that confuse pests
PULL Principle
Attractive Effect: Attractive plants or traps divert pests away from the main crop.
- Trap plants as "sacrificial crops"
- Pheromone traps
- Color traps (yellow and blue sticky boards)
The Synergy Effect of the Combination
The combination of both strategies creates a dual effect: pests are simultaneously pushed away (Push) from the main crop and pulled towards (Pull) the trap plants. This method is environmentally friendly, sustainable and significantly reduces the use of chemical pesticides.
Advantages of Push & Pull in Hydroponics
Biological Protection
Reduces chemical residuesHigher Resistance
Diverse modes of actionSustainability
Long-term effectivenessCost Efficiency
Lower treatment costsFirst article in the series: Push & Pull Introduction
Sprouts
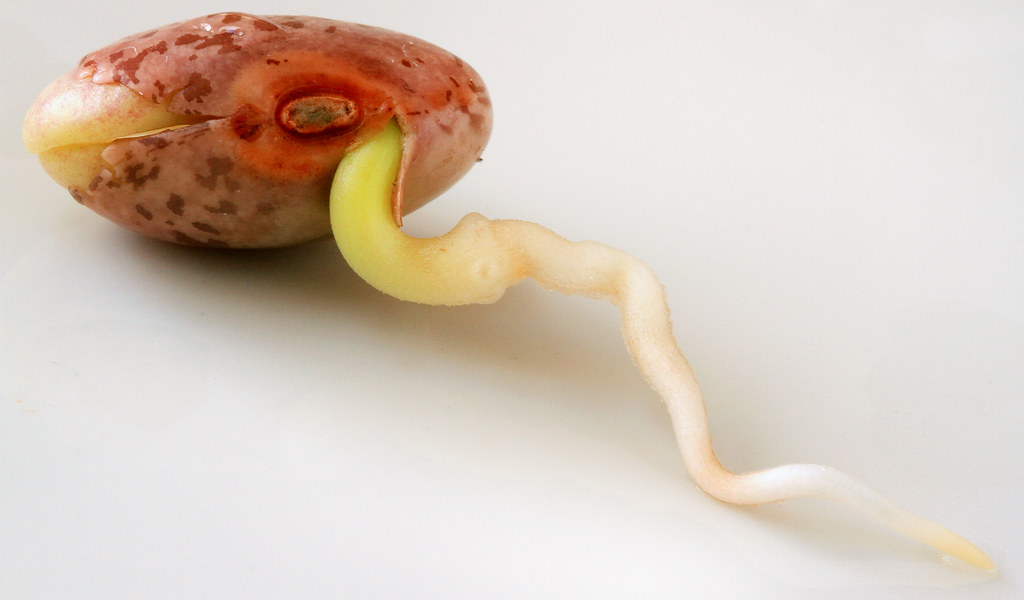

Sprouts are the first stage in the development of seeds. Most seeds are very healthy at this stage. The sprouting of grains, nuts, beans and seeds has been a common practice in countries such as East Asia and Europe for literally thousands of years. In fact, various forms of soaking, sprouting and fermenting seeds have been part of almost every culture in one way or another.
Important
Some sprouts are difficult to digest raw or may even contain toxins. Some toxins (Solanine) are not destroyed even by intense heating (cooking, frying, etc.). More on this here. Consumer protection even advises against consumption for certain population groups altogether.
Quote: The results show that microbiological hazards are present when consuming fresh sprouts and seedlings. In particular, consumers with weakened immune systems (for example, children, seniors, pregnant women) should therefore generally refrain from eating fresh sprouts and seedlings. Read the full article from the Lower Saxony State Office for Consumer Protection here.
Sprouts can easily be grown at home. Only water, the seeds and a sprouting container are needed. There are various cultivation methods to successfully grow the seeds. For non-mucilaginous seeds, sprouting devices or a sprouting jar are best suited. For mucilaginous seeds, you should use a cress sieve or combine fleece paper and a sprouting device. Non-mucilaginous seeds need to be watered thoroughly one to four times a day. The mucilaginous seeds, on the other hand, may only be sprayed with water once a day. These are not suitable for the sprouting jar!
KAT ID: 37